Understanding Motor Planning in Sensory Disorders
Understanding Motor Planning in Sensory Disorders
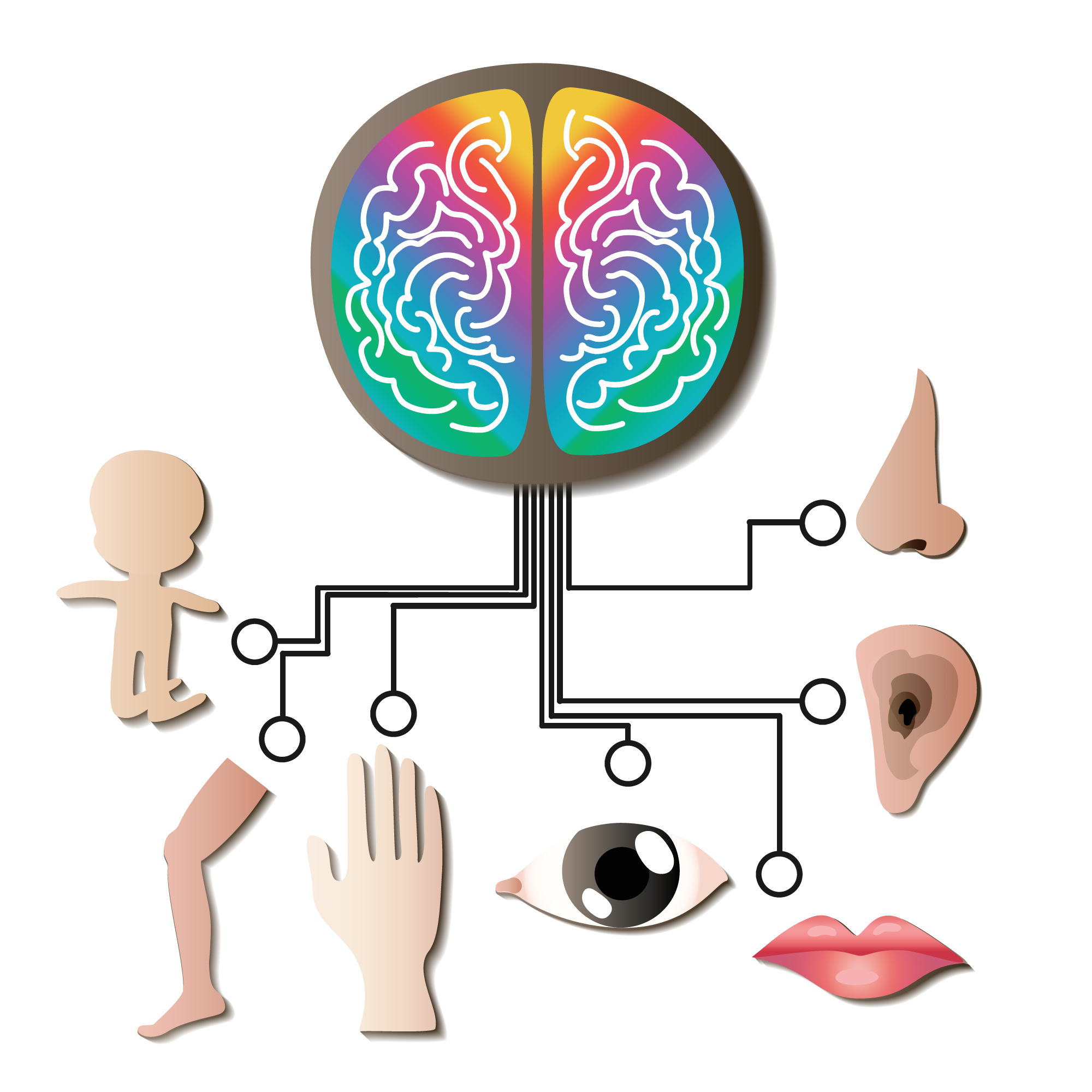
Motor planning, or praxis, is the ability of the brain to conceive, organize, and execute skilled, non-habitual motor acts. Each day, we perform a wide range of actions that require the integration of sensory information and the preparation of motor movements. However, for individuals with sensory disorders, this complex process can present significant challenges. The following strategies and therapies are designed to enhance motor planning skills, providing individuals with the tools to navigate the world more effectively.
Sensory Integration Therapy
Sensory integration therapy is a specialized technique aimed at helping individuals process and organize sensory information. By incorporating specific activities that provide varied sensory input, this therapy stimulates the central nervous system, encouraging the development of efficient neural pathways. Activities might include swinging, brushing, or deep pressure touch, each tailored to the individual’s specific sensory issues.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is often a cornerstone of motor planning improvement, especially when focused on fine motor skills and coordination. OT sessions for individuals with sensory disorders are highly individualized, with activities that range from simple, such as threading beads, to complex, like planning and executing a multi-step craft project.
Weighted Objects and Specialized Equipment
The use of weighted objects or specialized equipment can provide the necessary sensory feedback to enhance motor planning. For example, a child with sensory processing disorder might find the use of a weighted pencil beneficial in maintaining control and pressure when writing. Similarly, specialized seating or desk arrangements can provide support and stability necessary for body awareness and coordinated movement.

Visual and Auditory Cues
Visual and auditory cues can be instrumental in assisting individuals with sensory disorders to organize their movement patterns. Incorporating tools like visual schedules, color-coded instructions, or metronome therapy can help provide a predictable rhythm and structure, key elements for effective motor planning.

Environmental Modifications
Individuals with sensory disorders often struggle when environments are overwhelming. Environmental modifications, such as acoustic treatments to reduce noise, or organizing a workspace to minimize visual clutter, can improve the individual’s ability to focus on motor tasks, thus reducing cognitive overload and stress.

Routine and Predictability
Establishing a routine is especially beneficial for individuals with sensory disorders. The predictability of tasks helps reduce anxiety, setting the stage for improved motor planning. A consistent schedule and the same order of activities each day can be invaluable, as the brain becomes more efficient at planning and executing these sequences over time.

In summary, interventions for motor planning in sensory disorders must take a multi-faceted approach, combining sensory integration with occupational therapy and environmental accommodations. These strategies are not only designed to improve motor skills but also to enhance the individual’s overall quality of life, fostering greater independence and participation in daily activities. As we continue to learn and adapt, the field of sensory and motor disorder treatment will undoubtedly evolve, offering hope and support to those who need it most.










 Speech Therapy
Speech Therapy Physical Therapy
Physical Therapy Occupational Therapy
Occupational Therapy